 Photo #: STS028-88-26 Date: Aug. 1989
Photo #: STS028-88-26 Date: Aug. 1989Geographic Region: USA-WASHINGTON
Feature: MOUNT SAINT HELENS

 Photo #: STS028-88-26 Date: Aug. 1989 Photo #: STS028-88-26 Date: Aug. 1989Geographic Region: USA-WASHINGTON Feature: MOUNT SAINT HELENS |
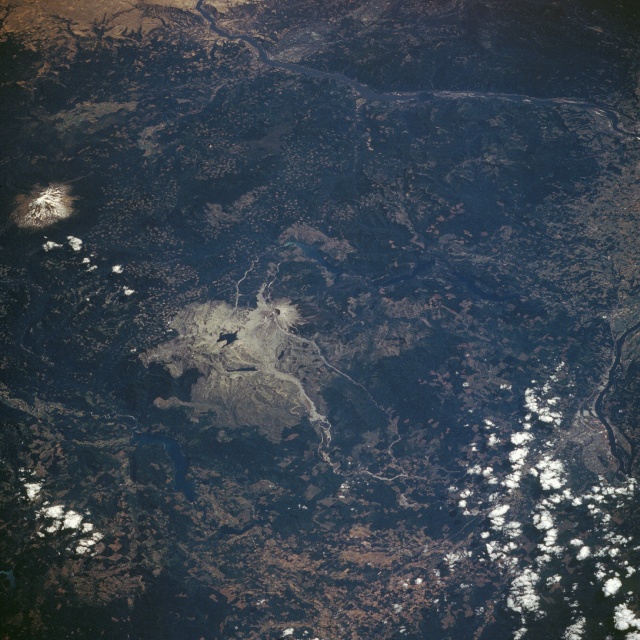 |
| STS028-088-026 Mount Saint Helens National Volcanic Monument, Washington, U.S.A. August 1989 Mount Saint Helens volcano and its 230-square-mile (370-square-kilometer) blast zone from the May 18, 1980, eruption can be seen in the center of this low-oblique, southeast-looking photograph. Called the "Fire Mountain" by the Klickitat Indians, Mount Saint Helens is the most frequently active and violent volcano in the 48 contiguous states. Prior to the 1980 eruption, the volcano last erupted during a period from 1835 through 1857. A sharp earthquake on March 2, 1980, marked the mountain's return to life after 123 years of relative quiet. On May 18, 1980, a strong earthquake of 5.1 magnitude triggered one of the most horrific landslides in recorded history. The bulging north face of the volcano began to move, peeled away, and produced an avalanche of superheated water, volcanic rock, and blocks of glacial ice. Within seconds of the avalanche, a plume of black smoke appeared above the broken crater, followed by a rush of steam. Great forces pushed this superheated cloud of ash [estimated to be near 680 degrees Fahrenheit (360 degrees Celsius)] and fragmented rock downhill toward Spirit Lake (visible north of the volcano). The ash cloud also billowed upward soaring to 70 000 feet (21 350 meters) into the atmosphere. Nearly every living thing within the blast zone was annihilated. Mount Saint Helens lost over 1300 feet (397 meters) of elevation. Spirit Lake stabilized at an elevation of 200 feet (64 meters), which is higher than before the eruption because the lake bottom filled with debris from the avalanche. The mud and ash flow that occurred during the eruption can be seen as a grayish area within the floodplain of the North Toutle River, which extends westward from the volcano. A large dam has been constructed on the river 16 miles (25 kilometers) west of the base of the volcano to help prevent further catastrophic flows of mud and ash downstream, should there be a future eruption. Mount Adams, a snow-covered, dormant volcano at 12 276 feet (3744 meters) and the second highest peak in the Oregon and Washington Cascade Range, can be seen 35 miles (58 kilometers) east of Mount Saint Helens. The Columbia River, separating the states of Washington and Oregon, is visible to the south and southeast of the volcano. Surrounding the volcano, clear-cut patterns caused by lumbering are interspersed throughout the dark green, forested regions of the Gifford Pinchot National Forest. |
| Images: | All Available Images Low-Resolution 191k |
|
| Mission: | STS028 |
|
| Roll - Frame: | 88 - 26 |
|
| Geographical Name: | USA-WASHINGTON |
|
| Features: | MOUNT SAINT HELENS |
|
| Center Lat x Lon: | 46.0N x 122W |
|
| Film Exposure: | N | N=Normal exposure, U=Under exposed, O=Over exposed, F=out of Focus |
| Percentage of Cloud Cover-CLDP: | 10 |
|
| Camera:: | HB |
|
| Camera Tilt: | LO | LO=Low Oblique, HO=High Oblique, NV=Near Vertical |
| Camera Focal Length: | 250 |
|
| Nadir to Photo Center Direction: | SE | The direction from the nadir to the center point, N=North, S=South, E=East, W=West |
| Stereo?: | N | Y=Yes there is an adjacent picture of the same area, N=No there isn't |
| Orbit Number: | 39 |
|
| Date: | 19890810 | YYYYMMDD |
| Time: | 222254 | GMT HHMMSS |
| Nadir Lat: | 48.2N |
Latitude of suborbital point of spacecraft |
| Nadir Lon: | 125.9W |
Longitude of suborbital point of spacecraft |
| Sun Azimuth: | 225 | Clockwise angle in degrees from north to the sun measured at the nadir point |
| Space Craft Altitude: | 163 | nautical miles |
| Sun Elevation: | 50 | Angle in degrees between the horizon and the sun, measured at the nadir point |
| Land Views: | VOLCANO, MOUNTAIN, FOREST, CRATER |
|
| Water Views: | RIVER, LAKE |
|
| Atmosphere Views: | |
|
| Man Made Views: | DEFORESTATION, URBAN AREA, DAM |
|
| City Views: | |
|
Photo is not associated with any sequences | ||
| NASA Home Page |
JSC Home Page |
JSC Digital Image Collection |
Earth Science & Remote Sensing |
|
|